Boiler
In viticulture, there are two types of heaters for heating must or wine: gas-fired and electric. Gas-fired heaters operate by combustion, reaching temperatures of up to 70°C, but with low energy efficiency and requiring safety measures. Gas boilers consist of a combustion chamber, an exchanger and a chimney to evacuate the gases.
Electric heaters use immersion heaters to heat the water, with regulation systems to control the temperature. Each system has advantages and disadvantages, depending on the fuel used.
Electric heaters use immersion heaters to heat the water, with regulation systems to control the temperature. Each system has advantages and disadvantages, depending on the fuel used.

Gas heater
The gas heater consists of an enclosure in which the must and wine circulate, heated by combustion. It can reach temperatures of around 50-60°C, with an output of between 35,000 and 95,000 W. However, it is not very energy-efficient (direct heating by combustion) and certain precautions need to be taken when using it correctly:
- Safety and regulation
- Eliminating odours and CO2
- Evacuation of combustion gases
- Insulation or protection of hot parts.
- No flow stop

Gas heater
Technical presentation
Oil and gas boilers are made up of three main parts:- A combustion chamber - or firebox - where the fuel burns in contact with the air.
- A heat exchanger where the heat produced by combustion is transferred to the water or fluid in the heating circuit
- A chimney where the combustion products are discharged.
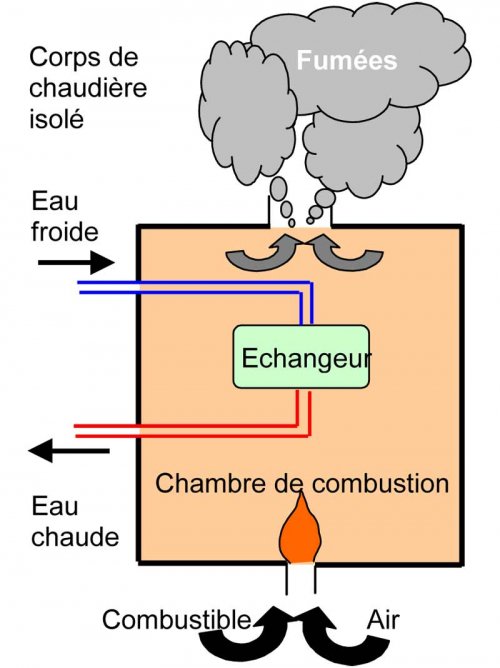
Schematic diagram of how a combustion boiler works
This appliance uses the principle of direct heating by combustion of a mass of water in which is placed an exchanger in which the must or wine to be treated circulates. This appliance is very easy to install and use, and can be used to develop high output (up to 100,000 kcal/h) for operations requiring large temperature variations (hot final maceration, etc.). This power is directly linked to the characteristics of the propane burners placed under the treatment tank and to the efficiency of the appliance (between 0.5 and 0.7).
These appliances should preferably be used outdoors to ensure that the burnt gases are properly evacuated, and should be fitted with a temperature regulator to cut off the gas at the desired temperature and a flow controller in the event of pump failure or clogged pipes.Gas heaters are supplied by the wine pumps used in the winery. The pumps and networks must be able to withstand temperatures of up to 70°C. The installation must be easy to clean and carry the CE mark.
These appliances should preferably be used outdoors to ensure that the burnt gases are properly evacuated, and should be fitted with a temperature regulator to cut off the gas at the desired temperature and a flow controller in the event of pump failure or clogged pipes.Gas heaters are supplied by the wine pumps used in the winery. The pumps and networks must be able to withstand temperatures of up to 70°C. The installation must be easy to clean and carry the CE mark.
Main components
The boiler body
When the boiler body (made of cast iron or stainless steel) is in operation, it heats up and emits heat by radiation. Insulation is therefore essential. Despite this, losses remain around a few percent.The burner
The best efficiency is obtained when the burner operates close to its rated output. For each boiler, the manufacturer recommends the burner that develops the flame best suited to the shape and size of the heat exchanger. This guarantees the performance of the installation.The chimney
Flue gases are made up of carbon dioxide, water vapour and other elements: nitrogen, sulphur derivatives (especially for fuel oil), chlorine, various unburnt substances and carbon monoxide.Depending on the boiler, certain standards must be taken into account by the installer or architect: height and diameter of the chimney to ensure sufficient draught for the flue gases, size of the installation room, ventilation, etc

Boiler
Special case of boilers with suction cups
The burner (A) and exchanger (B) are located in a sealed enclosure. The extractor (C), placed above the heating element, expels the combustion products to the outside, through the central pipe of the suction cup (D), at the same time as it draws in the air needed to operate the burner from the periphery, through a concentric pipe.The boiler can therefore be installed anywhere, even in a small room with no chimney, ventilation or aeration. The outlet is directly through the wall.
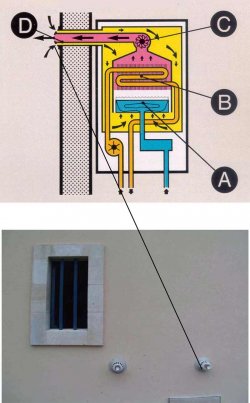
Diagram and photo of a suction boiler
Special case of forced-air burners
This type of burner is identical in principle to oil burners, differing only in the control and safety devices. Unlike atmospheric burners, these burners are equipped with a combustion head that ensures an intimate mixture of air and gas. Ignition is by high-voltage electrode, so there is no pilot light. The power range is much greater and efficiency higher, but at the expense of quiet operation.Fuels
Domestic fuel oil
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Easy to use Burns at room temperature Easy to obtain |
Price fluctuates |
Natural gas
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Easy to use No stock to manage, no risk of supply shortages |
Price varies according to location and quantity consumed Connection options depend on distance from the network and consumption Subscription |
Butane and propane
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Easy to use | Tank storage with annual rental or consignment Stock management Prices fluctuate according to company, customer, consumption, etc Risk of supply disruption (bad weather, etc.) |
Note : The fuel must match the burner, boiler and settings. Any change of fuel with a multi-fuel burner must be accompanied by a new setting.
Electric heater
Technical presentation
Two possible diagrams:- The water in the buffer tank is heated directly using one or more immersion heaters.
- The water in the buffer tank circulates in a secondary network comprising one or more heaters connected in series or in parallel.
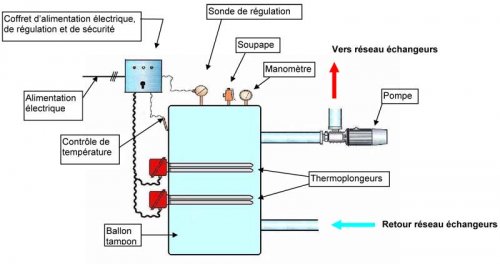
Electric heating inside the storage tank
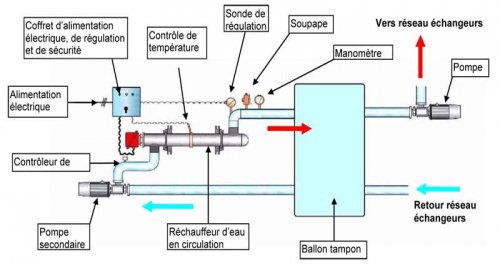
Electric heating with secondary network
Main components
The immersion heater (also known as the heating rod) is the element that heats the water circulating in the in-line heater or directly in the storage tank.
The material must be chosen to resist scaling and corrosion (stainless steel or VLY).
The heating element or storage tank, preferably made of stainless steel, must be insulated. It must be earthed.
The material must be chosen to resist scaling and corrosion (stainless steel or VLY).
The heating element or storage tank, preferably made of stainless steel, must be insulated. It must be earthed.

Immersion heater
Regulation
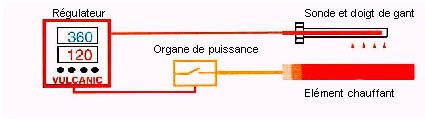
The temperature sensor (thermocouple, Pt100) measures the temperature of the circulating water in real time.
The electrical and control cabinet supplies power to the immersion heater and regulates the water temperature by setting a setpoint temperature and an alarm temperature.
The electrical and control cabinet supplies power to the immersion heater and regulates the water temperature by setting a setpoint temperature and an alarm temperature.
Control system
